Can you list the predictors of a difficult airway?
1. Difficult Bag-Mask Ventilation
Mnemonic = MOANS
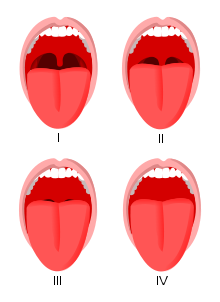
Mallampati classification
2. Difficult Laryngoscopy and Intubation
| Mask seal | Bushy beards, crusted blood on the face, or disruption of lower facial continuity |
| Obesity / Obstruction | Obesity, pregnancy, angioedema, Ludwig’s angina, upper airway abscess, epiglottitis |
| Age | Age > 55 |
| No teeth | May leave denture in edentulous patients. |
| Sleep apnea / Stiff lungs | COPD, asthma, ARDS, others |
Mallampati classification
Mnemonic = LEMON
| Look externally | Use your clinical gestalt, evidence of lower facial disruption, bleeding, small mouth, agitated patient |
| Evaluate | Use the 3-3-2 rule: mouth open, mandible, glottis |
| Mallampati score | In order of increasing difficulty Class I-IV |
| Obstruction / Obesity | Four cardinal signs of upper airway obstruction: stridor, muffled voice, difficulty swallowing secretions, sensation of dyspnea. Obese patients frequently have poor glottic views. |
| Neck mobility | May not be able to optimally move the head and neck due to trauma, arthritis, ankylosing spondylitis. Immobilize the neck and consider using video laryngoscopy. |
Mnemonic = RODS
| Restricted mouth opening |
| Obstruction |
| Disrupted or Distorted airway |
| Stiff lung or cervical Spine |

Difficult Cricothyrotomy
Mnemonic = SHORT
| Surgery or other airway obstruction |
| Hematoma (includes infection/abscess) |
| Obesity |
| Radiation distortion (and other deformity) |
| Tumor |
There are no absolute contraindications to performing an emergency cricothyrotomy.
References
Walls R, Murphy M. Chapter 7: Identification of the Difficult Airway. Manual of Emergency Airway Management. Third Edition. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins
1. Image source
2. Image source
3. Image source
4. Image source









